Get Started with AWS Lambda
You can connect to Upstash database from your Lambda functions using your favorite Redis client. You do not need any extra configuration. The only thing to note is you should use the same region for your Lambda function and database to minimize latency.
If you do not have any experience with AWS Lambda functions, you can follow the following tutorial. The tutorial explains the required steps to implement an AWS Lambda function that takes the key/value as parameters from APIGateway then inserts an entry (key/value) to the database which is on Upstash. We have implemented the function in Node.js, but the steps and the logic are quite similar in other languages.
note
This example uses Redis clients. Check this article to use REST API inside AWS Lambda.
Step 1: Create database on Upstash
If you do not have one, create a database following this guide.
Step 2: Create a Node project
Create an empty folder for your project and inside the folder create a node project with the command:
npm initThen install the redis client with:
npm install ioredisNow create index.js file. Replace the Redis URL in the below code:
var Redis = require("ioredis");
if (typeof client === 'undefined') { var client = new Redis(REDIS_URL);}exports.handler = async(event) => { await client.set("foo", "bar"); let result = await client.get("foo"); let response = { 'statusCode': 200, 'body': JSON.stringify({ result: result, }) } return response};Step 3: Deploy Your Function
Our function is ready to deploy. Normally you could copy-paste your function code to AWS Lambda editor. But here it is not possible because we have an extra dependency (redis-client). So we will zip and upload our function.
When you are in your project folder, create a zip with this command:
zip -r app.zip .Now open your AWS console, from the top-right menu, select the region that you created your database in Upstash. Then find or search the lambda service, click on Create Function button.
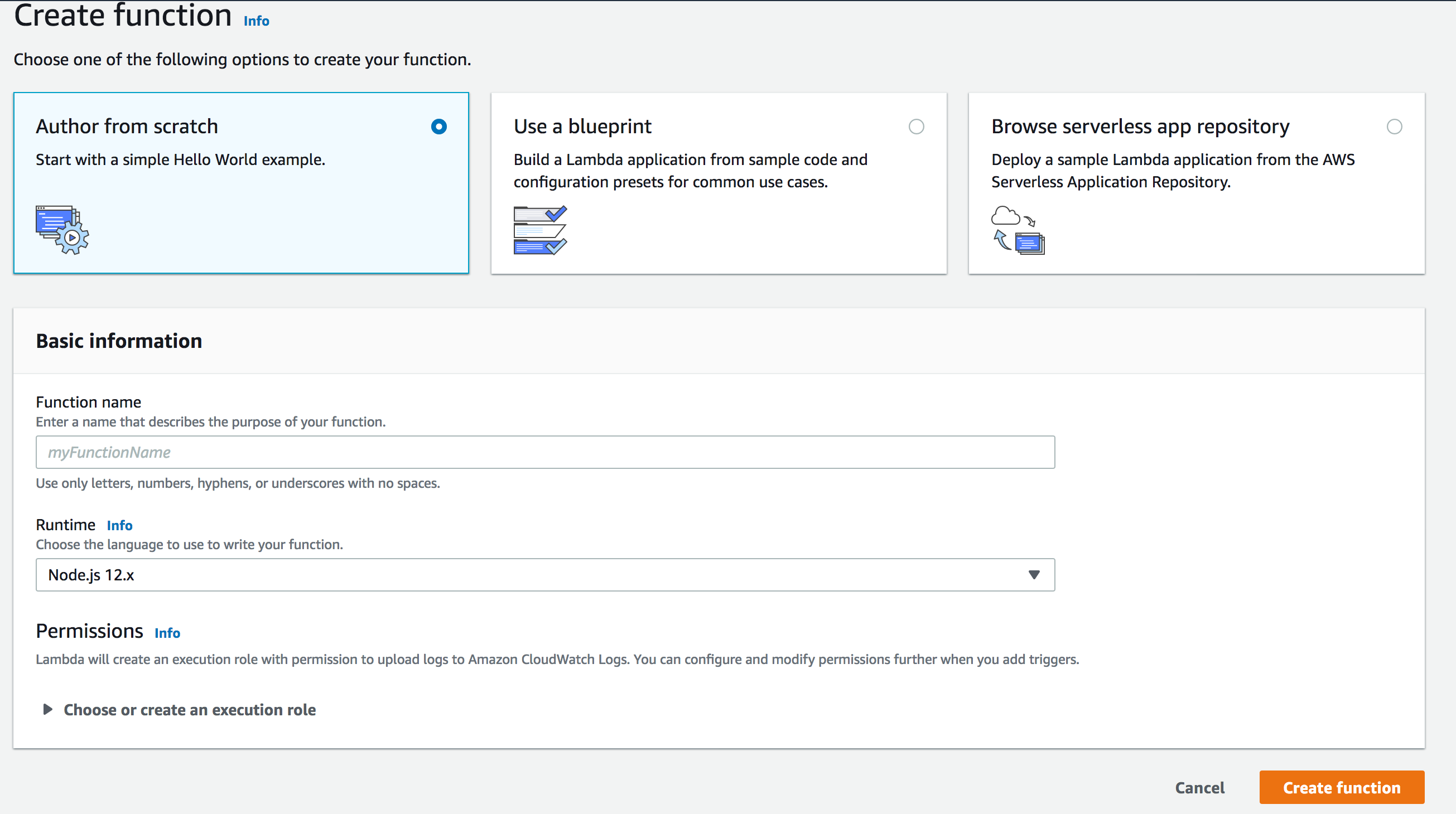
Enter a name for your function and select Node.js 14.x as runtime. Click Create Function.
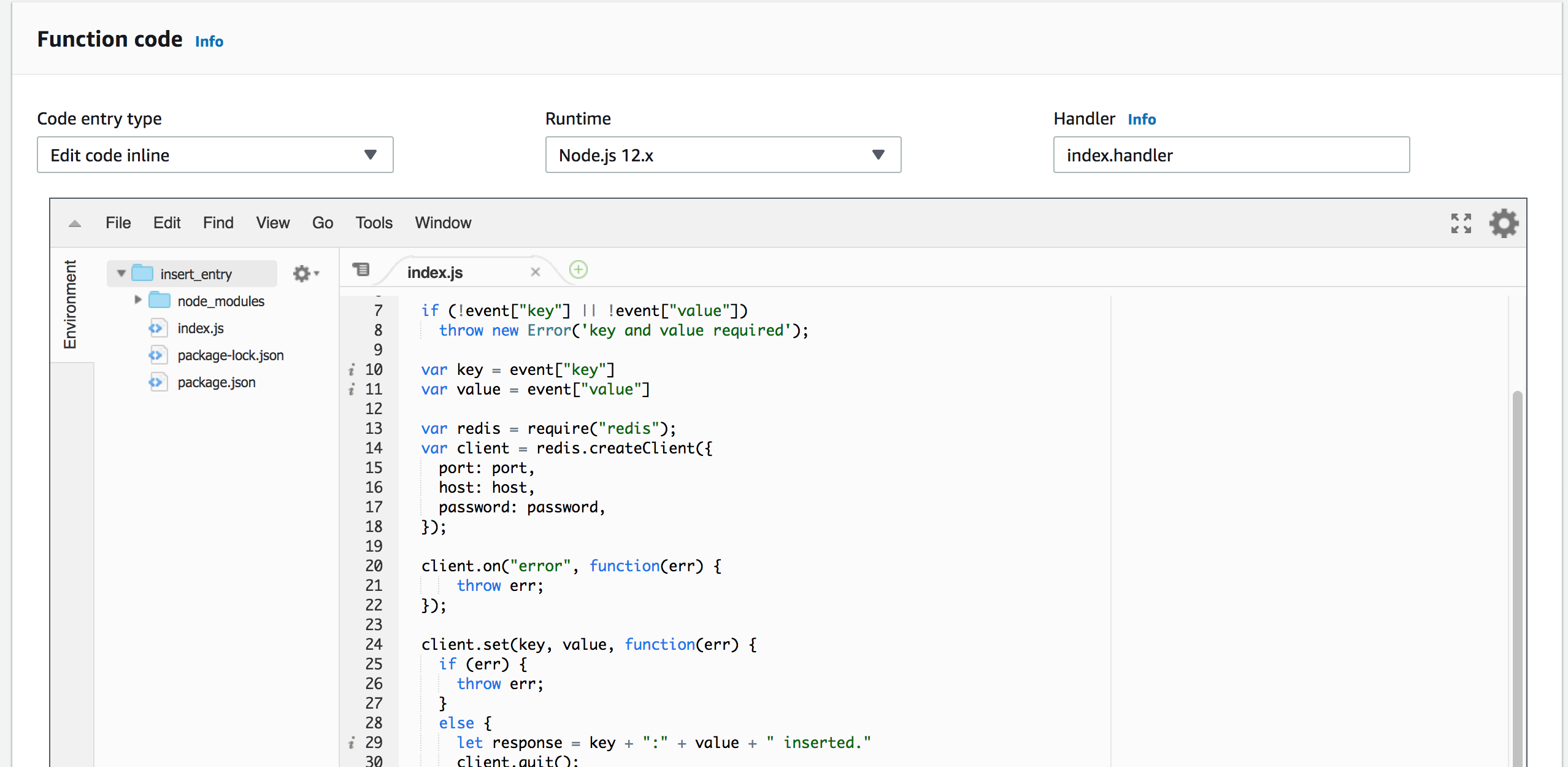
Now you are on the function screen, scroll below to Function Code section. On Code entry type selection, select Upload a .zip file. Upload the app.zip file you have just created and click on the Save button on the top-right. You need to see your code as below:
Now you can test your code. Click on the Test button on the top right. Create an event like the below:
{ "key": "foo", "value": "bar"}Now, click on Test. You will see something like this:
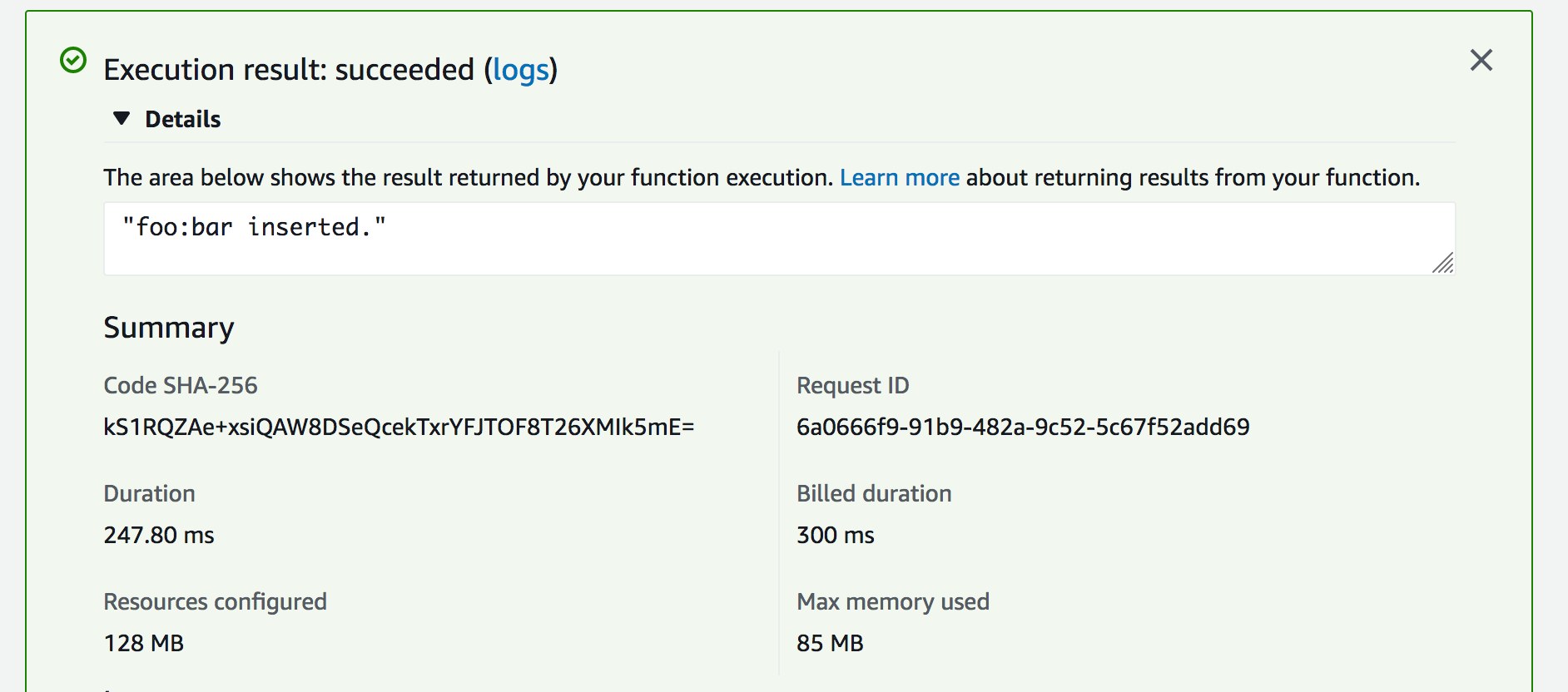
Congratulations, now your lambda function inserts entry to your Upstash database.
What can be the next?
- You can write and deploy another function to just get values from the database.
- You can learn better ways to deploy your functions such as serverless framework and AWS SAM
- You can integrate API Gateway so you can call your function via http.
- You can learn about how to monitor your functions from CloudWatch as described here.
Redis Connections in AWS Lambda#
Although Redis connections are very lightweight, a new connection inside each Lambda function can cause a notable latency. On the other hand, reusing Redis connections inside the AWS Lambda functions has its own drawbacks. When AWS scales out Lambda functions, the number of open connections can rapidly increase. Fortunately, Upstash detects and terminates the idle and zombie connections thanks to its smart connection handling algorithm. Since this algorithm is used; we have been recommending caching your Redis connection in serverless functions.
info
See the blog post about the database connections in serverless functions.
Below is our findings about various Redis clients' behaviours when connection is created, a single command is submitted and then connection is closed. Note that these commands (AUTH, INFO, PING, QUIT, COMMAND) are not billed.
| Client | #Commands | Issued Commands |
|---|---|---|
| redis-cli | 2 | AUTH - COMMAND |
| node-redis | 3 | AUTH - INFO - QUIT |
| ioredis | 3 | AUTH - INFO - QUIT |
| redis-py | 1 | AUTH |
| jedis | 2 | AUTH - QUIT |
| lettuce | 2 | AUTH - QUIT |
| go-redis | 1 | AUTH |